Only 28% of a sales rep’s time is spent on actual selling, with the rest consumed by administrative tasks, often due to outdated tools and manual processes. For MSPs, adopting modern sales strategies is essential to maximize efficiency and drive revenue growth.
This guide provides a comprehensive framework for MSP sales success, from selecting and training skilled sales teams to leveraging modern quote to cash tools like CPQ software and client portals to streamline workflows. You’ll also learn how to target the right customers, tailor service bundles, and track critical metrics.
Whether you're refining your processes or starting from scratch, this comprehensive guide will equip you with actionable insights to build and maintain a strong MSP Sales Team.
MSP Definition
An MSP, or Managed Service Provider, is a technology company that manages the IT infrastructure and end-user systems for other businesses. MSPs offer a range of services, including network management, security, monitoring, and maintenance, typically provided under a subscription or contractual agreement
What is MSP Sales?
Managed Service Provider (MSP) sales involve offering managed IT services to businesses, either by augmenting their existing IT teams or taking on a more comprehensive role in managing their IT needs. MSP sales focus on delivering business value and maintaining strategic relationships by providing recurring services that prevent downtime, enhance security, and ensure smooth operations. These services can address gaps in skill or capacity, whether on a long-term basis or as part of a specific project.
How to Select and Train MSP Sales Staff
Developing a high-performing sales team requires a thoughtful approach to selecting the right talent and providing them with the training and support needed to grow their expertise.
The cornerstone of building sales expertise starts with hiring individuals who have the potential to excel in sales roles. Look for candidates who:
- Have strong communication and problem-solving skills
- Are adaptable and resilient
- Flexible and persistent
To identify these qualities during the hiring process, incorporate behavioral interviews, role-playing exercises, and skill assessments. Evaluate not only their technical abilities but also their cultural fit within your organization, ensuring they align with your company’s values and can work collaboratively across teams.
Interview Questions for MSP Sales
- How do you approach selling a service vs a tangible product?
- Can you walk me through your process for identifying and qualifying potential clients?
- Give an example of a time you successfully navigated a complex sales cycle with multiple decision-makers.
- What strategies do you use to stay informed about industry trends and evolving IT challenges to better serve your clients?
- How do you approach building and maintaining relationships with clients in a competitive B2B environment?
Training and Building Sales Expertise
Once you’ve selected the right people, focus on building their expertise through comprehensive training. Effective training programs should combine technical knowledge, soft skills development, and hands-on experience.
Training
Start with a program that equips your team with both the knowledge and skills they need to excel:
- Know Your Business Value: Your team should deeply understand the services you provide and the unique value they bring to customers. This goes beyond just knowing the offerings. Recognize what sets your business apart, why customers choose you, and why they’ll want to partner with you for the long term. Provide resources like service guides, case studies, and competitor comparisons.
- Master the Process and Tools: Teach your team how to navigate consultative or solution-based selling methodologies and train them on essential tools.
- Customer-Centric Techniques: Focus on skills like active listening, asking insightful questions, and handling objections with confidence. Help them build trust and close deals while keeping the customer’s goals front and center.
- Hands-On Practice: Reinforce learning with role-playing exercises, shadowing, and real-world simulations. Feedback loops are critical for fine-tuning techniques and building confidence.
- Understand the Customer: Equip your team with a clear understanding of your ideal customer profile (ICP) and buyer personas. This includes knowing your customers’ pain points, goals, industries, and decision-making processes. Tailoring the approach to these details ensures more meaningful conversations and stronger connections.
Continuing Education
Training doesn’t end after onboarding; continuous development ensures your team stays ahead of industry trends and market demands. Foster a culture of learning through these strategies:
- Mentorship and Collaboration: Pair less experienced salespeople with seasoned veterans who can provide guidance, share insights, and offer constructive feedback. Create a supportive environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their experiences, successes, and lessons learned.
- Continuing Education: Provide access to online courses, webinars, and industry events. Encourage participation in workshops and conferences to keep the team informed about market trends and best practices.
- Goals and Feedback: Establish clear, measurable sales targets and regularly review performance. Deliver actionable feedback to help team members focus on areas for improvement and celebrate their progress.
- Knowledge Sharing Platforms: Implement tools and forums where team members can share resources, tips, and strategies. Hosting regular knowledge-sharing sessions fosters collaboration and innovation.
- Recognition and Motivation: Celebrate both small and significant achievements through incentive programs, public acknowledgment, and team-wide celebrations. Recognition boosts morale, reinforces positive behavior, and motivates the team to excel.
How to Create an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) 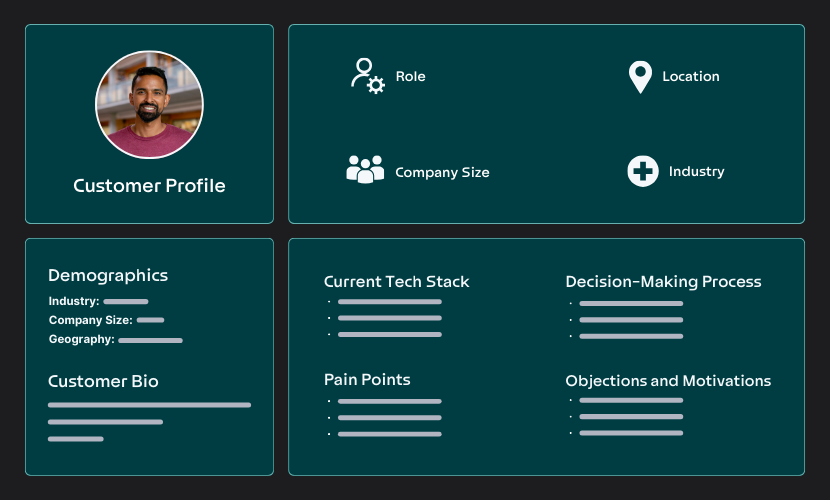
Creating an ideal customer profile (ICP) is a crucial step in refining your sales strategy as an MSP. It helps you understand who your ideal customers are, what their pain points are, and how your services can best meet their needs.
With a detailed customer profile, your sales team can deliver more personalized solutions, improving both customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
Identify the Key Demographics
Start by gathering basic demographic information about your potential customers. This helps create a foundational understanding of who they are. Key data points include:
- Industry: What industry does the company belong to? Different industries have different IT needs (e.g., healthcare may prioritize security, while retail might focus on inventory management).
- Company Size: Is the company a small startup or a large enterprise? Smaller companies might need more basic support, while larger organizations may require advanced solutions.
- Geography: Where is the business located? This affects their IT infrastructure needs and the type of support they require.
Understand Their Pain Points
To truly connect with potential clients, it's essential to know their specific challenges. These are the problems that your MSP can solve. Ask yourself questions like:- Are they struggling with network security issues?
- Is scalability a challenge for them as they grow?
- Are they using outdated systems and looking for a more modern solution?
- Are they experiencing downtime that affects their productivity?
- Are they struggling to keep up with existing demand?
- Do they have skillset gaps?
Map Out Their Current Technology Stack
A big part of MSP sales is knowing what technology your potential customers are already using. This helps identify gaps and opportunities for your services. Focus on:- What hardware and software are they using?
- Are they using cloud services, and if so, which providers?
- What security measures are in place?
- Do they have a dedicated IT team or are they relying on external support?
Define Their Decision-Making Process
Understanding how your customer makes purchasing decisions is key to closing the deal. Some businesses may have a formal decision-making process with multiple stakeholders, while others might have a more streamlined approach.
- Who is involved in the purchasing decision
- What are their criteria for selecting a vendor?
- What is their budget for IT services?
Create Customer Personas
To make this all actionable, compile your findings into detailed customer personas. These are semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers, based on the data you've gathered. Each persona should include:- Name and role: Create a name and role for each persona (e.g., "Tech-Savvy Tim," an IT director at a medium-sized healthcare firm).
- Pain points and goals: What keeps them up at night? What are their key business goals
- Objections and motivations: What could hold them back from purchasing your services? What would motivate them to make a change?
Refine Your Profile Over Time
A customer profile is not a one-and-done task. As you learn more about your customers and the market, continuously update your profiles. Gather feedback from your sales team, analyze your sales data, and stay aware of shifts in your target industries. This ongoing refinement ensures your customer profiles remain relevant and accurate.
MSP Sales Strategies
A strong MSP sales strategy focuses on creating digital-first experiences that engage customers and simplify decision-making. At the heart of this approach is the proposal, a critical piece that can make or break a deal. By prioritizing polished, professional proposals alongside modern tools, MSPs can build trust, close deals faster, and drive meaningful growth. Here’s how to make it happen:
Guided Selling
Guided selling provides customers with a clear path to navigate complex purchasing decisions. Tailored workflows simplify options, making it easier for customers to choose the right solutions. This approach not only enhances their experience but also positions your MSP as a trusted advisor.
Digital Sales Rooms
Digital sales rooms create a collaborative environment where deals move forward with less friction. Customers can:
- Review proposals and documents in real time.
- Communicate directly within the sales process.
- Track progress with full transparency.
This interactive, digital approach improves alignment and keeps the momentum going.
Unified Client Portals
Unified client portals offer a single, accessible location for everything your customers need. They can track ongoing projects, send and receive updates, and review proposals without delay. By fostering efficiency and transparency, these portals strengthen the customer relationship and improve satisfaction.
Spotlight on Proposals
Proposals are often the deciding factor in a deal. With standardized templates for proposals and statements of work (SOWs), MSPs can ensure:
- Faster delivery times.
- Professional and consistent presentation.
- Clear, actionable content that drives decisions.
A well-executed proposal process not only builds confidence but also accelerates deal closures while leaving a lasting impression.
Flywheel Sales Model for MSPs

The traditional sales funnel is a familiar model for visualizing the customer journey and while it’s still a valuable tool, it has its limitations. Funnels focus on moving customers through stages, but they don’t emphasize what happens after conversion or how to sustain momentum.
The flywheel model prioritizes reducing friction and creating ongoing momentum by aligning sales, marketing, and service efforts. Instead of seeing the customer journey as linear, the flywheel focuses on continuous engagement and growth. Here’s how the flywheel applies to MSP sales:
Attract
- Help prospects identify their IT challenges through educational content like blogs, webinars, and workshops.
- Use thought leadership to position your MSP as a trusted advisor.
Engage
- Offer guided selling to match prospects with the right services and solutions.
- Provide digital experiences like client portals and real-time proposal tools to reduce decision-making friction.
Delight
- Deliver on your promises with top-tier customer service and proactive IT support.
- Use retention-focused strategies like managed services, subscriptions, and ongoing account reviews to keep customers satisfied and loyal.
The more you implement these strategies, the faster the wheel begins to spin and the more your business grows. Unlike the funnel, the flywheel doesn’t stop at conversion. It creates a cycle of customer satisfaction and loyalty that fuels continuous growth.
MSP Sales Process Stages

The sales process provides the steps to take at each stage of the funnel to move prospects closer to a decision. Here’s an overview of the key stages:
Step 1: Lead Generation/Prospecting
Identify potential customers through digital marketing, referrals, and networking. Build a pipeline of leads aligned with your ideal customer profile.
Step 2: Qualifying Prospects
Evaluate leads to ensure they have the budget, authority, need, and timeline for your services.
Step 3: Initial Contact
Establish a connection through email, phone, or meetings. Introduce your value proposition and gather insights about the prospect’s IT challenges and goals.
Step 4: Presentation
Showcase how your solutions address the prospect’s needs. Use customized proposals to highlight the benefits and ROI of your services.
Step 5: Closing the Deal
Finalize the agreement, address objections, and confirm terms. Ensure a smooth transition to onboarding.
Step 6: Follow-Up and Loyalty Programs
Maintain relationships through regular check-ins, exceptional service, and loyalty incentives. Identify opportunities for renewals, upselling, or cross-selling.
Tools to Keep Track of MSP Sales Progress
To effectively monitor sales progress, MSPs need the right tools to streamline workflows and track key metrics. Here are the essentials:
- CRM Software: Manage customer data, track interactions, and monitor deal progress.
- Sales Pipeline Tools: Visualize deal stages and prioritize high-value opportunities.
- CPQ Software: Guided selling, quote tracking, standardized workflows, real-time pricing and availability, automated proposals and agreements, deal approvals, digital sales rooms, and automated hand-offs.
- Analytics Platforms: Measure KPIs like win rates, deal velocity, and revenue trends.
- Collaboration Tools: Coordinate tasks and improve team communication.
Instead of cobbling together multiple tools that may not work seamlessly and drain your time and resources, TechGrid provides a platform that connects and optimizes your existing tech stack while giving you automated sales tools to build, sell, and fulfill technology solutions online.
With features like sales and fulfillment workflows and embedded technology finance, TechGrid simplifies the process of managing sales, proposals, and service delivery. Designed from real-world MSP experience, it integrates your entire tech stack, allowing you to deliver the right solutions quickly and efficiently while minimizing risks and maximizing flexibility.
Sales Incentives and Compensation Plans for MSP Sales Teams
Motivating MSP sales teams requires clear and rewarding comp plans that align with business goals. Here are key approaches:
- Base Salary + Commission: Provide financial stability with a base salary and incentivize performance through commission on closed deals.
- Tiered Commission: Increase commission rates as sales targets are surpassed to reward high performers.
- Bonuses for Recurring Revenue: Tie bonuses to growth in monthly recurring revenue (MRR) to drive subscription sales.
- Incentives for Cross-Selling/Upselling: Offer higher rewards for selling value-added services like cloud or cybersecurity solutions.
- Team-Based Rewards: Encourage collaboration with group bonuses for meeting shared revenue goals.
Key MSP Sales Metrics

Tracking the right metrics helps MSPs optimize their sales processes and drive growth. Here are four critical metrics:
- Median Recurring Revenue (MRR): Reflects the average monthly revenue from subscriptions, providing insight into financial stability and customer retention trends.
- Average Deal Size: Measures the value of signed contracts, highlighting profitability and opportunities to adjust pricing or upsell services.
- Time to Close: Tracks the average duration of closing deals, identifying inefficiencies in the sales process and helping to accelerate cash flow.
- Close Ratio: Calculates the percentage of won deals compared to total opportunities, offering a clear view of sales efficiency and the effectiveness of your team's efforts.
Monitoring these metrics ensures your sales strategy remains efficient and aligned with growth objectives.
3 Sales Hacks You Should Be Using (and One You Shouldn’t)
The right sales strategies can transform your MSP business. Here are three proven hacks to improve your sales process, and one common mistake to avoid.
Hack 1: Connect Your CPQ Process to a Digital Services Catalog
Integrating CPQ software with a digital catalog streamlines quoting for IT services and eliminates common inefficiencies.
- Time to Quote: Automate manual steps to create quotes faster.
- Pricing Consistency: Standardize service offerings for reliable pricing.
- Productivity: Reduce admin work and errors with integrated tools.
A digital catalog with price automation makes accurate, scalable, and repeatable quotes a reality.
Hack 2: Bundle and Package Solutions
Simplify decision-making for customers by bundling complementary services into comprehensive packages.
- Combine offerings like cloud solutions, help desk support, and cybersecurity.
- Adopt as-a-Service (XaaS) models to integrate product and service sales, driving predictable recurring revenue.
- Use automated CPQ workflows to seamlessly combine products and services.
Hack 3: Leverage Partnerships to Scale
Expand your capabilities and reach by building a structured partner network.
- Expand Geographic Reach: Partners help you break into new regions and markets.
- Enhance Skill Sets: Tap into your partners’ expertise to win bigger deals and meet diverse client needs.
- Scale Workforce: Use partners to scale for larger projects without committing to permanent staff.
Don’t: Rely on Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets may feel like the familiar, comfortable choice for managing sales—the devil you know—but they quickly become a massive bottleneck and a liability as your business scales.
- Time-Consuming: Manually updating spreadsheets slows down your team, reducing the time they can spend on high-value tasks like selling and building relationships.
- Error-Prone: One wrong formula or forgotten update can lead to inaccurate quotes, missed deadlines, or inconsistent pricing—problems that can damage customer trust.
- Lack of Visibility: Spreadsheets don’t offer a centralized view of sales activity or real-time insights, making it hard to track deals, measure performance, or adjust strategies.
- Collaboration Challenges: Sharing and editing spreadsheets across teams can lead to version control issues and confusion, creating unnecessary friction in your sales process.
Switching to an automated, centralized platform eliminates these issues. By connecting your quoting, proposals, and sales data in one system, you can ensure accuracy, save time, and enable your team to focus on what matters most: closing deals. Spreadsheets might feel familiar, but they’re holding your sales team back.
Glossary of Terms
Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads or opportunities that successfully convert into paying customers. A key indicator of the effectiveness of your sales and marketing strategies.
Consultative Selling: A sales approach where the focus is on relationship building and understanding the client’s unique needs and challenges. Instead of pushing products or services, the MSP acts as a trusted advisor, offering tailored solutions that align with the client's goals.
Sales Velocity: The speed at which opportunities move through the sales funnel and convert to closed deals. Higher sales velocity indicates an efficient sales process.
Cost per Lead (CPL): The average cost of generating a single lead, calculated by dividing total marketing expenses by the number of leads generated. Helps measure the efficiency of lead generation campaigns.
Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs): Leads that have been vetted and are ready for direct engagement by the sales team. These leads show strong interest and are a good fit for your services.
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs): Leads that have interacted with your marketing materials and shown potential interest in your services, requiring further nurturing before they become SQLs.
Pipeline Stage Conversion Rates: The percentage of opportunities that progress from one stage of the sales pipeline to the next. This metric highlights areas for improvement in the sales process.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The projected revenue a customer will generate over their entire relationship with your business. Helps assess the long-term profitability of your customer base.
Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who discontinue their subscriptions or contracts over a given period. A high churn rate indicates potential issues with service quality or customer satisfaction.
Lead Response Time: The average time it takes to respond to a new lead. Faster response times increase the likelihood of conversion.
Proposal Acceptance Rate: The percentage of proposals sent that result in a closed deal. A strong indicator of the effectiveness of your proposal process.
Upsell and Cross-Sell Rates: The frequency at which existing customers purchase additional or upgraded services. Indicates success in growing revenue from current clients.
Forecast Accuracy: The difference between projected and actual sales results. High forecast accuracy reflects a solid understanding of your sales pipeline and market.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer, calculated by dividing total sales and marketing expenses by the number of new customers acquired in a period.
Win Rate: The percentage of sales opportunities that result in closed deals. A key measure of your sales team's effectiveness.
Sales Growth: The measure of revenue increase over a specific period. This indicates the success of sales strategies and the overall growth of the MSP business.
Sales Opportunities: Potential customers who have expressed interest in your services and are being actively pursued by your sales team. Tracking opportunities helps predict revenue and prioritize leads.
Quote-to-Close: The ratio of quotes sent to deals closed. This metric helps identify the effectiveness of your pricing, proposals, and overall sales approach.
Age of Opportunity: The amount of time a sales opportunity has been open. Analyzing this metric helps prioritize deals and identify patterns for improving close rates.
Response Time: The time it takes for sales reps to respond to inquiries or follow up with leads. Faster response times often improve the chances of closing deals.
Total Pipeline Dollars: The total value of all sales opportunities in your pipeline. This metric helps forecast revenue and evaluate the health of your sales pipeline.
Website Visitors: The number of users visiting your website within a given period. It’s a key metric for understanding the reach and effectiveness of your online presence.
Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may indicate poor content relevance or website usability issues.


